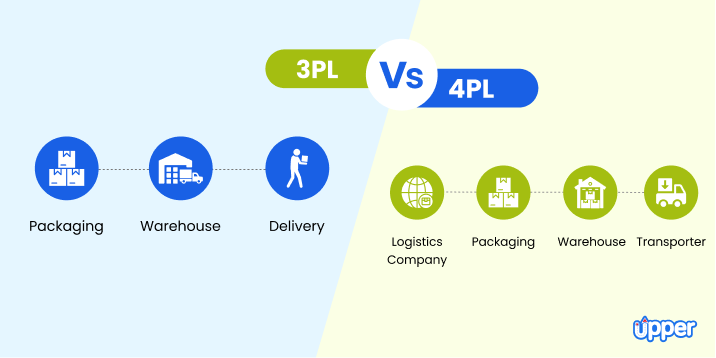
Related Posts
Want to Streamline your Delivery Business Process?
Sign Up with Upper Route Planner and automate your daily business process route planning, scheduling, and optimizing!
Wait!
Grab a FREE Trial of Upper
×
- Plan routes with hundreds of stops in a minute
- Schedule routes months in advance
- Collect reliable proof of delivery
- Track drivers live for real-time updates
- Experience unparalleled customer support
Wait!
Grab a FREE Trial of Upper TODAY!
×
- Plan routes with hundreds of stops in a minute
- Schedule routes in advance for weeks
- Collect proof of delivery to maintain accountability
- Experience 24/7 customer support
- Smart reporting to get real-time insights
Wait!
Grab a FREE Trial of Upper TODAY!
×
- Plan routes with hundreds of stops in a minute
- Schedule routes in advance for weeks
- Collect proof of delivery to maintain accountability
- Experience 24/7 customer support
- Smart reporting to get real-time insights
×